Several regulations and rules have been put in place for manufacturers and products in various industries. The factories have to follow these regulations to be recognized (as valid) by the organizations that set up those rules. One body of rules strictly adhered to is the RoHS compliance directive. The RoHS directive was implemented by the European Union to put a check on the products that enter the European Union market.
RoHS 2.0 compliance is essential, mainly, for the electronic and electrical industries. However, the compliance test does not exclude the umbrella market. This article will tell you everything you need to know about the RoHS 2.0 test and its relation to umbrellas.
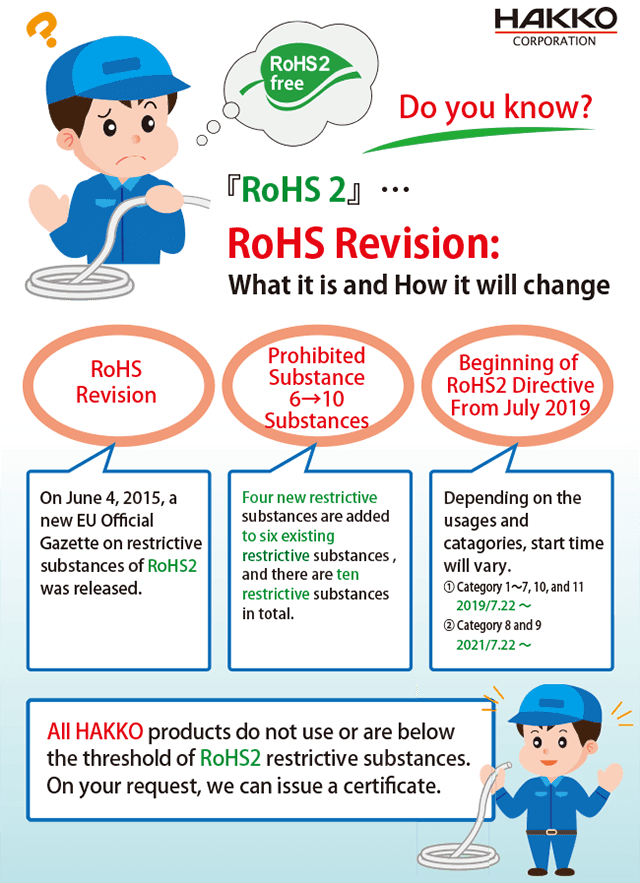
Table of Contents
What is RoHS 2.0?
The European Union adopted the Restriction of Hazardous Substances or RoHS (also known as Directive 2002/95/EU) in 2003. The law of RoHS encompasses the handling of hazardous materials, from manufacturing these materials to their disposal. RoHS arose out of the need to reduce potential hazards and the impact of wastes from electric and electronic equipment on the environment.
RoHS has developed a very effective way to address the EU’s growing concern at the increase in Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). This begins with restricting the use of hazardous substances at the point of manufacture. The RoHS directive reduces the likely risks of dermal, oral, and nasal exposure to harmful products.
Since its inception in 2003, RoHS has had some upgrades such as RoHS 2.0 and RoHS 3. Each upgrade comes with new additions to the original RoHS to make electrical and electronic products less harmful for both the workers and users of these products. For instance, the original RoHS restricted the use of six hazardous materials found in electrical and electronic products. But in RoHS 2.0 and 3, there were more additions of prohibited substances.
RoHS 2.0 is known as Directive 2011/65/EU. It is also called RoHS-Recast. This directive was published in 2011 by the EU. On the 21st of July 2011, there was the implementation of RoHS 2.0. RoHS-Recast has had a lot of impact on the electronics industry and electrical products. The process needed to obtain the RoHS 2.0 certification is pretty straightforward for companies to follow. That way, it does not seem too difficult to follow through with the regulations. Organizations prove that they are RoHS 2.0 compliant by producing a letter of compliance issued by an employee of the RoHS Company.
The RoHS 2.0 directive applies to manufacturers, authorized representatives, importers, and distributors of certain products. The products in this category include large household appliances, small household appliances, computing and communications equipment, consumer electronics, lighting, power tools, toys, sports equipment, automatic dispensers, monitoring, and control instruments.
RoHS 2.0 does not only apply to manufacturers of electronic and electrical equipment but also the metal industry. RoHS 2.0 applies to the metal industry because of the application of metal plating, anodizing, chromating, etc., on electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) components.
Although RoHS 2.0 compliance was created inside Europe for members of the European Union, other parts of the world have employed and created their forms of the RoHS. This includes Asian countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, etc., and North America.
A country like China has its version of RoHS compliance. The China RoHS is also known as the Administrative Measure on the Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic Information Products (ACPEIP). The ACPEIP took effect on the 1st of March, 2007. The China RoHS also ensures that products are compliant with the restricted substances provided by the EU RoHS.
It is advisable to seek a third-party company that would provide test reports of the materials, material declarations directly from the supplier, and Declarations of Conformity. This would aid in acquiring the RoHS certification. The third-party inspection services or companies could help point out where there might be room for company improvements. It is then left to the manufacturing company to make these necessary changes.
There are two main areas of risk that RoHS 2.0 compliance focuses on:
- The product material risk involves selecting materials and components to manufacture the Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE). RoHS 2.0 is also interested in the use of indirect materials in the process of manufacturing.
- The supplier risk focuses on product variation, engineering changes, multiple suppliers, and contamination from the supply chain.
Aims of RoHS 2.0
The aim of RoHS 2.0 was to:
- Develop better regulatory conditions. And by better, we mean simple, effective, and enforceable regulations.
- Align and harmonize RoHS with other European Union legislation.
- Prevent risks directed at human health and the environment, with a focus on the workers.
- Increase the level of legal clarity and certainty.
Differences between RoHS and RoHS 2.0
- There was a gradual extension in the scope of requirements to all EEE in RoHS 2.0, in contrast to RoHS.
- There is a better clarification of important definitions in RoHS 2.0 as against RoHS.
- RoHS 2.0 added new items to the list of restricted substances in the RoHS provision. RoHS 2.0 also allowed member states to propose new substance restrictions.
- RoHS 2.0 allows for more precise and more transparent rules for granting, deleting, or renewing exemptions.
- RoHS 2.0 is more coherent with other EU legislation than RoHS.
RoHS 2.0 Directive’s Restricted Substances
These restricted materials are considered very dangerous to the environment. They pollute landfills and are hazardous in the area of occupational exposure during manufacturing and recycling.
The recognized restricted substances in the RoHS 2.0 directive include:
- Lead (Pb): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Mercury (Hg): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Cadmium (Cd): <100 ppm or 0.01%
- Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
- Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP): <1000 ppm or 0.1%
NOTE: ppm stands for ‘parts per million.’
For products to be deemed compliant with the RoHS 2.0 directive, they should not exceed the restricted substances’ limits.
What is CE Mark?
The Conformitè Europëenne (CE) Mark is known to be the European Union’s conformity mark designed to regulate the goods sold within the European economy. The CE mark shows that the manufacturer has assessed a product, and it ms the EU’s requirements. Safety, health, and environmental protection as the basis of the assessment.
The products that need to go through the CE marking process are those that, although they are manufactured anywhere globally, are marketed in the European Union. It is forbidden to put the CE mark on products that do not comply with all the relevant requirements, such as RoHS 2.0 compliance.
The CE mark on a product also indicates that there is appropriate technical documentation that supports the manufacturer’s claims of safety. This documentation should be readily available to be presented by the manufacturer, importer, or person responsible for placing the product on the European Union market.
RoHS 2.0 includes a CE marking directive. In other words, RoHS compliance is necessary for the CE marking of products. Companies that manufacture electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) or devices must comply with RoHS 2.0 before using the CE mark on their products.
Exceptions to the RoHS 2.0 Directive
There are some notable exemptions to the RoHS 2.0 directive, and they include:
- Military equipment
- Batteries and packaged materials
- Large-scale permanent installations
- Solar panels
- Medical devices
- Large-scale immobile industrial tools
Why Should the Umbrella Need the RoHS 2.0 Test?
You may wonder why an umbrella would need to go through the RoHS 2.0 compliance test, even though it does not belong to the category of electronic and electrical equipment. Here are some reasons why this test is necessary for the umbrella:
- To Reduce Instances of Heavy Metal Poisoning
One of the main reasons why the EU put the RoHS 2.0 directive in place for certain products was to reduce poisoning. Since most e-waste (that is, discarded electrical or electronic devices) is transported to factories and manufacturers in third-world countries, the factories’ workers suffer cases of lead and mercury poisoning. Heavy metal poisoning is not peculiar to only the workers in umbrella factories and the users of the umbrellas. RoHS 2.0 ensures that umbrella factories and other producers of EEE make use of lead-free solders and components. As a result of this, there is a reduction in heavy metal poisoning cases during umbrella usage.
- For Product Reliability
Many factories and manufacturers are adopting the RoHS 2.0 compliance directive nowadays, with umbrella manufacturers not exempted. These manufacturers participate in RoHS 2.0 because they want their customers assured of the safety of their products. A product that passes the RoHS 2.0 screening is considered reliable by its consumers. Once a manufacturer can prove that their products are safe and trustworthy, their reliability status is improved tremendously.
- Umbrellas Contain Components That Have the Restricted Substances
In the manufacturing of umbrellas, some parts of the umbrella contain some of RoHS 2.0 substances’ restrictions. And as such, the umbrellas have to undergo this screening. This screening would ensure that those substances are not higher than the allowed quantity by the RoHS 2.0 directive. For instance, there could be lead in the paints used for the umbrella’s canopy, and some umbrellas make use of metal plating in the umbrella’s shaft. In the cases mentioned above, there is a need for the umbrellas to pass through the RoHS 2.0 test to ensure that the restricted substances are not in excess; that is, they do not exceed the stipulated limit.
- For Ease of Trade Within the EU
The European Union has made the RoHS 2.0 directive a criterion for any manufacturer who hopes to trade within the EU. In other words, as an umbrella manufacturer, if you wish to sell and distribute your umbrellas in the European Union market, it is vital that your umbrellas are RoHS 2.0 compliant and that they obtain the RoHS 2.0 credentials.
- To Get the CE Mark
The Conformitè Europëenne (CE) mark shows that a product has been assessed and proven to meet the European Union’s safety, health, and environmental requirements. Any umbrella with the CE mark represents the manufacturer’s declaration that the product complies with the EU’s directives. That is, the CE mark shows that a product meets the specified European Union conformity regulations. And for a product to get this CE mark, it has to pass the RoHS 2.0 compliance test.
- Some Umbrellas Fall Under the Category of Leisure and Sports Equipment
There are specific categories of manufacturers that have to go through the RoHS 2.0 compliance testing. And some umbrellas fit under one or two of these categories. For instance, patio umbrellas fit under the leisure category, while golf umbrellas are under the sports equipment division. So, specific umbrellas like these have to prove they are compliant with the RoHS 2.0 directive essentially.
How to Test an Umbrella by RoHS 2.0
When an umbrella is to be tested by RoHS 2.0, its components and the materials used in the manufacturing process are analyzed. Let’s review how to test an umbrella by RoHS 2.0 using the results from testing our products. The following are the parts of the umbrella that went through testing and a breakdown of the examination.
1. Wood Handle
An official tested the wooden handle of the umbrella for Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg), Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI), Polybrominated Biphenyls and Diphenyl Ethers (PBB and PBDEs), and all the Phthalates. In each instance, except for the Phthalates, the x-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) result indicated that the substances were below the required limit. The XRF test determines whether or not the restricted substances found in a product are below the limit. The wood handle did not contain any phthalate. The overall outcome of the wooden handle test was that it passed.
2. Screw
The RoHS 2.0 directive tested screw for Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr VI, PBB, PBDEs, and the phthalates, which were put in a group. Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury were below the limit in the XRF test. However, Hexavalent Chromium was marked “X”; this indicates that further investigation would need to be carried out. PBB, PBDEs and the phthalates did not have a reading. The conclusion: the screw passed the test.
3. Umbrella Bag
The substances tested for in the umbrella bag were Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Hexavalent Chromium, Polybrominated Biphenyls, and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. These substances were below the limit placed by the European Union. On the other hand, Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate, Benzyl Butyl Phthalate, Dibutyl Phthalate, and Diisobutyl phthalate were not detected by the XRF.
4. Magic Stickers
The test that was done for the magic stickers resulted in a “pass.” The test was carried out to determine the level of Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium, Polybrominated Biphenyls, Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers, and the Phthalates. All the restricted substances, except all the phthalates, were under the XRF screening limit.
5. Silver Plastic
The silver plastic on the umbrella is usually used to line the inner canopy of the umbrella. The silver plastic acts as protection from the sun for the umbrella user. The substances tested for in the silver plastic include Lead (Pb), Cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg), Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI), Polybrominated Biphenyls and Diphenyl Ethers (PBB and PBDEs), which were all below the limit in the XRF testing. The Phthalates were not detected in the umbrella’s silver plastic.
6. Silver Plastic Button
In the X-Ray Fluorescence test carried out for the umbrella’s silver plastic button, the RoHS 2.0 compliance restricted substances were tested individually. The substances were: Lead (Pb), Mercury (Hg), Cadmium (Cd), Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI), Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB), Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE), Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP), Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP), Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP) and Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP). The phthalates, like in the other parts of the umbrellas, were not detected by the XRF.
7. Black Metal Bracket
The black metal bracket is used to give shape to the canopy of the umbrella. During the RoHS 2.0 compliance test, they detected Lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), Mercury (Hg), and Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI), but they were ‘below limit’ (BL). Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBB), Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDE), Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP), Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP), Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP), and Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP), however, were not detected at all.
8. Silver Metal Bracket
Lead and Mercury are two of the most common sources of heavy metal poisoning. For that reason, Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium, Polybrominated Biphenyls, Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers, and the Phthalates were tested for in the silver metal bracket. The first four substances were found in the silver metal bracket, and they were below the limit. The remaining substances were not found during the test. The conclusion was that the silver metal bracket passed the test.
9. Black Plastic Bottom Shell
The next test was carried out on the black plastic bottom shell. In this test, Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr VI, PBB, and PBDEs were lower than the limit set by the RoHS 2.0 test. On the other hand, DBP, BBP, DEHP, and DIBP (also known as the phthalates) were not detected during the examination. The conclusion of this test was a “pass.”
10.Wave Point Umbrella
Lastly, the Wave Point umbrella was tested during the RoHS 2.0 compliance test. The restricted substances tested in this stage were Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium, Polybrominated Biphenyls, Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers, Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate, Benzyl Butyl Phthalate, Dibutyl Phthalate, and Diisobutyl phthalate. The last four substances were not detected (ND), while the remaining six were Below the Limit (BL). The result of the test was that the wave point umbrella passed.
Summary of the Test
In summary, Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, and Hexavalent Chromium were below the required limits in all the parts of the umbrella that were tested. Polybrominated Biphenyls and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers were present in some features of the umbrella and absent in others. In the parts where they were existent, they were also below the limit.
However, the Phthalates, that is, Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP), Benzyl Butyl Phthalate (BBP), Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP), and Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP), were not detected throughout the test. The result of this test proved that the product is compliant with the directives of RoHS 2.0.
What is the Procedure to Test an Umbrella by RoHS 2.0?
There are four main stages involved in the procedure of testing an umbrella by RoHS 2.0. These stages are the documentation review stage, the process audit stage, the testing stage, and the certification statement stage. These stages will be discussed in detail below.
1. The Documentation Review Stage
In this stage, there is a review of the Bill of materials, the technical file, assembly drawings, and material declarations of each component of the umbrella. It is also at this stage that the test reports and conformance/compliance certificates are reviewed. These documents are obtained from all suppliers of the materials. The technical file that would be reviewed must contain:
- The general product description and design structure information
- Conformity information on materials, parts, and subassemblies
- Manufacturing documentation and records
- Risk assessment of materials, parts, and subassemblies
- Harmonized standards, specifications, and conformity procedures
This stage determines and verifies the current status of the documents and even the scope of testing needed.
2. Process Audit Stage
In the process audit stage, there is an inspection of the umbrella manufacturing process. A RoHS official would scrutinize every step from gathering materials needed in the manufacturing of the umbrella to its assembly. The manufacturing process must meet the RoHS 2.0 compliance with regards to the restricted materials.
3. Testing Stage
In the testing process, there is an on-site, portable X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) testing done to determine the values of the restricted RoHS substances. It is at this stage that substances like Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Hexavalent Chromium, phthalates, etc., are tested. Each part of the umbrella is examined to determine the amount of these substances detected in the umbrella. If the substances are found to be below the limit, then it is acceptable. On the contrary, if the substances’ values are above the required limit, they are considered hazardous.
4. Certification Statement Stage
The certification statement stage is the final stage in the testing of umbrellas with the RoHS 2.0 directive. After the previous processes have been completed and passed by the umbrella manufacturing company, a RoHS 2.0 Certificate of Compliance, also called Certificate of Conformity or Declaration of Conformity, is issued. The Certificate of Compliance is given as evidence of the completion of the RoHS 2.0 procedure.
Conclusion
Huifeng Umbrellas has been tested and found compliant under the RoHS 2.0 standards. Our products passed the various tests and are safe for use in the public. This goes to show our level of commitment to ensuring that our customers are safe and protected both in and out of the rain. We are certified with the CE mark, and our products are fit to be sold in the EU market and anywhere globally. You can rest assured that you would be safe from any poisoning when you purchase our umbrellas and have the best quality of products. What are you waiting for? Contact us today at info@hfumbrella.com.

